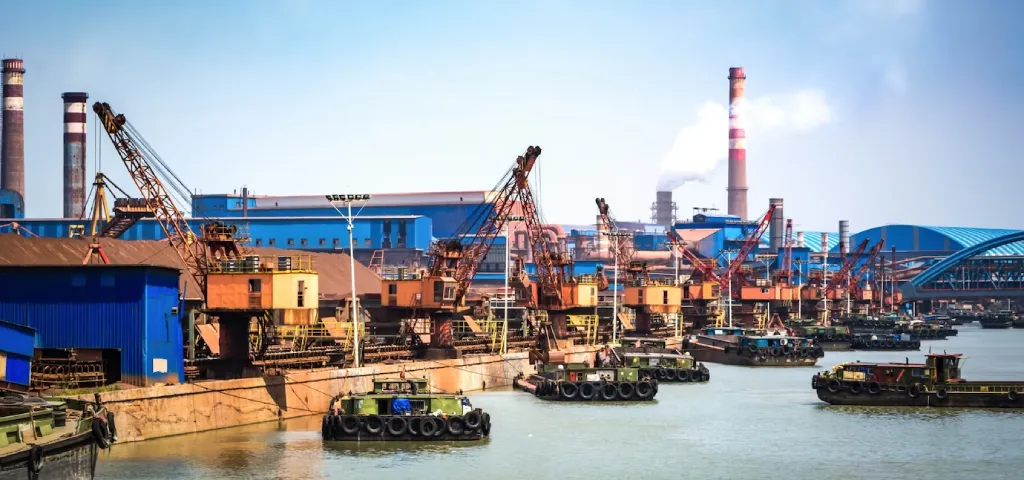
In recent years, the global business landscape has witnessed a profound shift in priorities, with Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors becoming increasingly pivotal in investment decisions. This transformation has been particularly pronounced in traditionally carbon-intensive sectors such as oil and gas. As investors seek sustainable, responsible, and ethical investments, the oil and gas industry has been prompted to adapt and address pressing ESG concerns.
Environmental Sustainability
The Pursuit of Net-Zero
Environmental sustainability remains a paramount concern within the oil and gas sector. The industry has been under scrutiny for its substantial carbon footprint, prompting companies to pledge commitments to achieve net-zero emissions. These commitments entail a multifaceted approach involving carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies, investment in renewable energy sources, and stringent emission reduction strategies.
Some leading oil and gas corporations have set ambitious targets to reach net-zero emissions by specific deadlines. They are actively investing in renewable energy projects, exploring cleaner extraction methods, and allocating substantial resources toward research and development in low-carbon technologies.
Social Responsibility
Stakeholder Engagement and Community Impact
Social responsibility has emerged as a key aspect of ESG in the oil and gas industry. Stakeholder engagement, including local communities, indigenous groups, and other relevant parties, has become integral in project planning and execution. Companies are increasingly focusing on fostering constructive relationships, respecting human rights, and mitigating the social impact of their operations.
Moreover, diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) initiatives have gained traction. Companies are striving to create more diverse workforces, ensuring equal opportunities for underrepresented groups, and enhancing workplace inclusivity. This emphasis on social responsibility extends beyond the organizational sphere to encompass the entire value chain.
Governance
Transparency, Accountability, and Risk Management
Effective governance practices are imperative for maintaining investor confidence and navigating the evolving ESG landscape. Transparency and accountability are crucial, with investors expecting clear communication regarding ESG goals, progress, and challenges faced by oil and gas companies.
Robust risk management strategies are also fundamental, especially considering the industry’s exposure to geopolitical, regulatory, and market risks. Companies are reevaluating their corporate governance structures, incorporating sustainability into boardroom discussions, and integrating ESG metrics into executive compensation frameworks.
Challenges and Opportunities
While the oil and gas sector is making strides in aligning with ESG principles, several challenges persist. One of the primary hurdles is the sheer magnitude of capital required to transition to cleaner energy sources and implement innovative technologies. Balancing profitability with sustainability initiatives remains a complex task, especially amid fluctuating commodity prices and regulatory uncertainties.
However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation and diversification. Companies investing in renewable energy projects, hydrogen production, and carbon capture technologies are positioning themselves to adapt to a future with increased emphasis on sustainable energy sources.
The Role of Investors in Driving Change
Investors play a pivotal role in accelerating the adoption of ESG practices within the oil and gas sector. As stakeholders demand greater accountability and transparency, investment decisions are increasingly influenced by a company’s ESG performance. Shareholder activism, engagement, and the integration of ESG criteria into investment strategies are driving forces compelling companies to prioritize sustainability.
Moreover, the emergence of ESG-focused funds and indices has provided investors with opportunities to allocate capital to companies that demonstrate a commitment to ESG principles. This trend has spurred competition among oil and gas firms to enhance their ESG profiles to attract investment and secure a social license to operate.
Conclusion
The trajectory of the oil and gas industry is undergoing a profound transformation shaped by ESG considerations. While challenges persist, there is a growing acknowledgment within the sector that embracing sustainability is not just a moral imperative but a strategic necessity. Companies that proactively adapt to the evolving ESG landscape by integrating sustainable practices into their core operations will likely be better positioned to thrive in a rapidly changing global economy.
As investors continue to prioritize ESG factors, their influence in steering the direction of the oil and gas sector towards a more sustainable future will undoubtedly remain a critical catalyst for change. The convergence of profitability and sustainability is becoming increasingly intertwined, heralding a new era where responsible practices are essential for long-term success in the oil and gas industry.