In an era where climate change concerns are at the forefront of global discussions, industries across the spectrum are being challenged to address their carbon emissions. Among these, the oil and gas sector, known for its significant carbon footprint, is actively seeking innovative solutions to mitigate its environmental impact. Carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) has emerged as a promising technology in the quest to reduce greenhouse gas emissions while sustaining energy production. This article delves into the potential of carbon capture solutions and their role in shaping the future of the oil and gas industry.
The Need for Carbon Capture in Oil & Gas
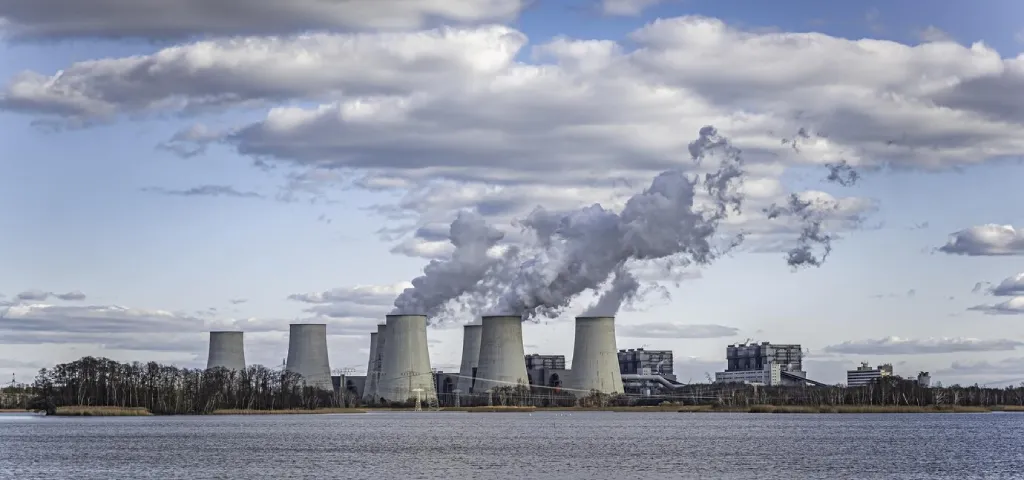
The oil and gas industry has long been a critical pillar of global energy production, meeting the world’s demands for transportation, electricity, and heating. However, its operations contribute significantly to CO2 emissions, amplifying concerns about climate change and environmental degradation. To combat these challenges without compromising energy security, the industry is turning to carbon capture solutions.
Carbon capture involves trapping CO2 emissions generated from industrial processes before they are released into the atmosphere. In the oil and gas sector, carbon capture can be integrated into various operations, such as during extraction, refining, and the utilization of hydrocarbons. By capturing CO2 at its source, this technology prevents it from entering the atmosphere, thereby curbing emissions and lessening the industry’s environmental impact.
Types of Carbon Capture Technologies
There are different methods employed in carbon capture, each with its own set of advantages and limitations. Three primary approaches include:
Pre-Combustion Capture
This method involves converting fossil fuels into a mixture of hydrogen and CO2 before combustion. The CO2 is then separated and captured before it is released into the atmosphere.
Post-Combustion Capture
Here, CO2 is captured after the fossil fuel is burned. This technology involves separating CO2 from other flue gases produced during combustion processes.
Oxy-Fuel Combustion
This technique involves burning fuel in oxygen rather than air, resulting in a flue gas primarily composed of CO2 and water vapor. CO2 is then separated from the water vapor and captured.
Integration of Carbon Capture in Oil & Gas Operations
The integration of carbon capture technologies into oil and gas operations is crucial for reducing emissions. From extraction sites to refineries and distribution networks, several areas present opportunities for implementation:
Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR)
Carbon capture can be used in EOR processes, where captured CO2 is injected into oil reservoirs to increase production while storing the greenhouse gas underground.
Refineries
Refining crude oil generates substantial CO2 emissions. Implementing carbon capture in this stage can significantly reduce these emissions by capturing CO2 from refining processes.
Gas Processing Units
Facilities that process natural gas often release CO2. Carbon capture systems in these units can help capture the CO2 for storage or utilization.
Transportation and Storage
Once captured, CO2 can be transported via pipelines to suitable geological formations for safe and permanent storage, preventing its release into the atmosphere.
Challenges and Opportunities
While carbon capture technologies hold immense promise, there are challenges hindering their widespread adoption. High initial costs, technological complexities, and the energy required for capturing and storing CO2 are among the hurdles. Additionally, the need for supportive policies and incentives to encourage investment in CCUS remains crucial.
However, advancements in technology, coupled with increasing global awareness of climate change, are driving innovations and collaborations. Governments, industries, and research institutions are investing in R&D to enhance carbon capture efficiency, reduce costs, and develop better storage solutions.
The Future Outlook
The oil and gas industry recognizes the urgency to transition toward more sustainable practices. Carbon capture solutions offer a viable pathway for the industry to decarbonize while ensuring energy security. Moreover, CCUS technologies can play a pivotal role in enabling the industry to meet emissions reduction targets set forth in various global climate agreements.
As technological advancements continue, the scalability and cost-effectiveness of carbon capture solutions are expected to improve. Collaborative efforts between governments, businesses, and innovators will be instrumental in accelerating the deployment of CCUS technologies across the oil and gas sector.
Conclusion
Carbon capture solutions present a promising avenue for the oil and gas industry to mitigate its environmental impact while continuing to meet global energy demands. By integrating these technologies into various stages of operations, the industry can significantly reduce CO2 emissions and contribute to the fight against climate change. With concerted efforts and continued advancements, carbon capture stands as a crucial pillar in shaping a more sustainable future for the oil and gas industry and the planet as a whole.